
RT Feeding is an important requirement in treating the elderly who can not have normal oral feeding. Most elderly people or seniors either have difficulties with eating or swallowing, as a result of illness, injury, or age-related conditions.
During these circumstances, rt feeding helps to keep the body fed with necessary nutritional and fluid needs as well as medication.
This reference will be aimed at patients, caregivers, relatives, and nurses at home who would desire a clear comprehension of RT Feeding and its care. In the hospital environment, as well as in the home, the ability to know the proper rt feeding procedure and safety measures can make a big difference in the lives and recovery.
The main purpose of Ryle’s tube feeding is to supply an appropriate level of nutrition in case of unsafe/insufficient intake using the mouth and ensure the patients stay strong, recover quicker, and prevent such complications as malnutrition or dehydration.
What is RT Feeding?
Ryle tube feeding, also referred to as RT Feeding, is a type of enteral nutrition. It entails inserting a thin, slim tube (Ryles tube) via the nose, through the food pipe (oesophagus), to the stomach or occasionally the small intestine.
As found in the elder care and nursing sources, rt feeding is normally applied as short to medium-term nutritional provision in case there is impairment of oral feeding.
How RT Feeding Works?
- The tube is transferred through the nose, oesophagus, and stomach
- Liquid food, water or medication can be administered into the stomach
- This avoids the mouth and swallowing mechanism, which is a source of risk of aspiration
General Tube Feeding vs RT Feeding
Although the term tube feeding is a generic term encompassing gastrostomy (PEG) or jejunostomy tube, RT Feeding is a specific term that involves the nasogastric feeding via a Ryle tube, which is neither surgical nor permanent.
Why is RT Feeding Needed?
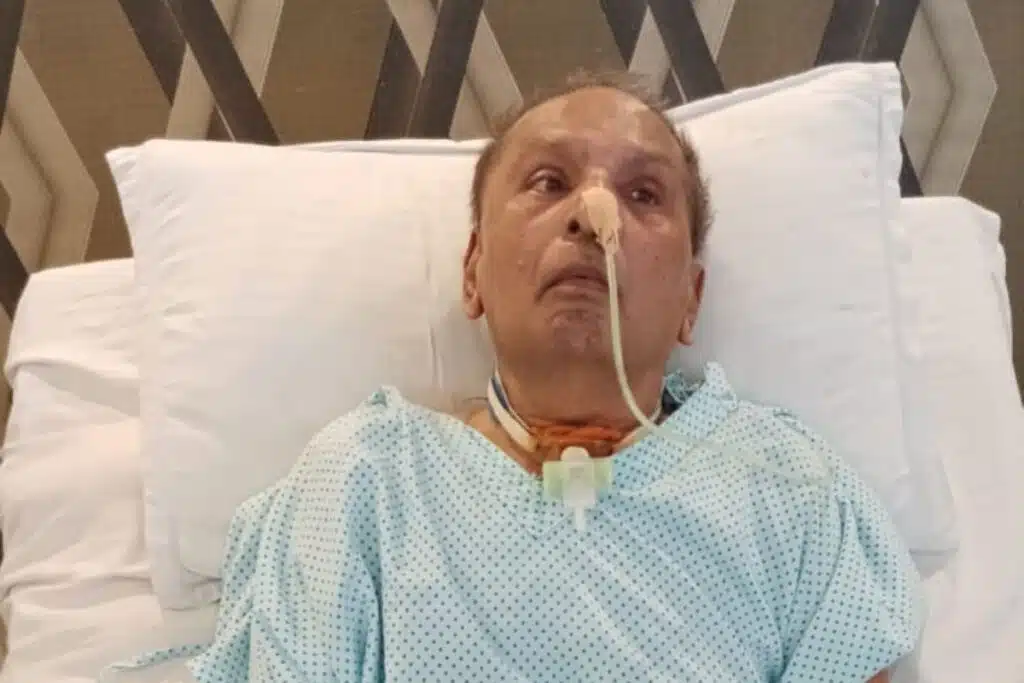
The use of RT Feeding is advised in cases where a patient is unable to sustain his or her nutritional needs by eating normal food. Medical conditions associated with this are:
- Swallowing Difficulties (Dysphagia): Aspiration is highly probable among patients who choke and cough during eating.
- Stroke and Neurological Disorders: Swallowing reflexes may be damaged by conditions such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease, ALS or brain injury.
- Post-Surgery Recovery: Patients might require RT Feeding after head, neck or gastrointestinal surgery.
- Critical Illness or Trauma: RT Feeding is usually required in ICU patients or patients on ventilatory support.
- Extreme Malnutrition or Lack of Oral Eating: RT Feeding will assist in feeding balance and convalescence.
Ryle tube feed is intended to ensure safe nutrition until oral feeding to the patient can be resumed.
RT Feeding Procedure
The knowledge of the rt feeding procedure is useful in making sure the process is safe and effective.
1) Before Insertion
- Nurse or doctor medical examination
- Write out the procedure for the patient
- Check nasal patency
- Gather sterile equipment
- Patient repositioning: upright or semi-Fowler position (45deg)
Routine placement and correct position of ryles tube feeding minimises pain and problems.
2) RT Tube Insertion
- Test tube length (nose to ear to stomach)
- Lubricate the tube
- Insert very tenderly through the nostril
- Request the patient to swallow in the process of insertion
- Insert the tube into the stomach
Placement Confirmation
- pH analysis of aspirated stomachs
- X-ray confirmation (gold standard)
To prevent lung feeding, this step is essential during rt tube insertion.
3) Feeding Methods
RT Feeding has three popular mechanisms:
Bolus Feeding
- Syringe to feed at regular intervals
- Mimics normal meal times
Gravity Feeding
- A feeding bag is used to feed at a slow rate
Pump-Assisted Feeding
- Feeding pump controlled delivery
- Frequent with the aged and the seriously ill
Nutrition and Technology of Medication
- Liquid formulae in commerce or prescribed rice tube feeding
- Medicines must be crushed (where possible) and diluted
- Empty the tube every time before and after medications
4) Tube Removal Criteria
- Patient is safe with an intact swallow
- Adequate oral intake
- Doctor’s approval
RT Feeding Uses
In most cases, Ryles tube uses include:
- When it is not possible to provide adequate nutrition during eating
- Safety in medication administration
- Ensuring hydration levels
- Promoting recovery
- Preventing weight loss and weakness in elderly patients
RT Feeding at Home Care: Step-by-Step Guide
Home rt feeding may be safe and effective when properly done.
Step 1: Preparation
- Wash hands thoroughly
- Prepare feed at room temperature
- Check tube position
Step 2: Patient Positioning
- Keep patient upright at 45–90deg
- Maintain position after feeding
Step 3: Administering the Feed
- Deliver feed slowly
- Avoid rushing
Step 4: After Feeding Care
- Flush the tube with clean water
- Close the tube securely
- Clean feeding equipment
Step 5: Daily Observation
- Watch for pain, swelling, or diarrhoea
- Observe nasal irritation
Adequate housekeeping leads to long-term success of RT Feeding.
RT Feeding Safety Measures & Possible Complications
RT Feeding is safe, but risks must be monitored.
Aspiration
- Never feed while lying down
- Confirm tube placement
Tube Blockage
- Flush the tube regularly
- Avoid thick, undiluted feed
Infection or Irritation
- Maintain hygiene
- Monitor nose and throat
Indications to Call Medical Personnel
- Difficulty breathing
- Persistent vomiting
- Tube displacement
- Severe abdominal pain
Conclusion
RT Feeding is a reliable and life-sustaining option for patients unable to eat normally. When performed correctly, it ensures nutrition, hydration, and medication delivery, supporting faster recovery.
With proper understanding and practice, caregivers can confidently manage RT Feeding, improving patient comfort and overall well-being.
Why Choose Gracias Living For Elder Care Services
At Gracias Living, Elder care services in Delhi NCR go beyond basic assistance—it is about ensuring dignity, safety, and comfort at every stage of aging.
With trained nursing professionals, doctor-guided care plans, and experience in managing complex needs such as RT feeding, post-stroke recovery, and mobility support, Gracias Living provides reliable and compassionate care for seniors.
Our focus on medical supervision, hygiene standards, and personalized attention makes us a trusted choice for families seeking dependable elder care services.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) What are RT feeds?
RT feeds refer to Ryle’s Tube feeding, a method of providing liquid nutrition, fluids, or medications directly into the stomach through a tube inserted via the nose. RT feeding is used when a person cannot swallow safely due to conditions like stroke, neurological disorders, or severe weakness.
2) Can RT feeding be done at home?
Yes, RT feeding can be safely done at home under medical guidance. With proper caregiver training, hygiene practices, correct patient positioning, and regular monitoring, home-based RT feeding is commonly used for elderly, post-stroke, or long-term care patients. Professional nursing support further reduces complications.
3) What are 5 uses of Ryle’s tube?
The five main uses of a Ryle’s tube are:
1) Providing nutrition when oral feeding is not possible
2) Administering medications
3) Maintaining hydration
4) Gastric decompression
5) Supporting recovery during illness or post-surgery
4) What are the risks of RT feeding?
Common risks of RT feeding include aspiration (food entering lungs), tube blockage, nasal irritation, infection, abdominal discomfort, and incorrect tube placement. Most risks can be minimized with proper positioning, regular tube flushing, hygiene, and medical supervision during feeding.
5) How to clean an RT feeding tube?
An RT feeding tube should be flushed with clean or sterile water before and after every feed or medication. Use a syringe to gently flush the tube to prevent blockages. The nostril area should be cleaned daily, and feeding equipment must be washed and air-dried properly.
6) How many days to change Ryle’s tube?
A Ryle’s tube is typically changed every 7 to 14 days, depending on medical advice, patient condition, and tube material. It may need earlier replacement if there is blockage, damage, displacement, or signs of infection. Always follow a doctor or nurse’s recommendation.




