
The memory loss may be terrifying, both when it occurs suddenly and partially or progressively over time. The two most common disorders relating to memory problems are amnesia and dementia, although most people confuse the two. The earlier one is informed about the difference, the earlier it can be diagnosed and cured, and one can find peace with the right senior care support.
This guide describes amnesia vs. dementia, their symptoms and causes, and the way to identify the early warning signs.
What Is Amnesia Disease?

Amnesia is a memory disorder that affects the memorizing and formation of memories in an individual. This is contrary to dementia, which does not have the propensity to affect intelligence, reasoning, and personality. In most cases, amnesia is abrupt and may be reversed through time, depending on the cause of the disorder.
Amnesia makes the person know about the individual, but they can hardly remember other events/conversations, or experiences. It can be either short-lasting or long-lasting, and the treatment is arranged to control and cure the symptoms and their cause.
Amnesia Symptoms
- Poor working memory of new events.
- Difficulties in developing new memories.
- Losing names, addresses, or discussions.
- Disorientation about schedules or orders.
- Asking the same questions again.
Types and Causes of Amnesia
- Anterograde amnesia—failure to create a new memory.
- Retrograde amnesia—forgetting the past.
- Transient global amnesia is impaired memory that is momentary.
Common causes include:
- Head injury or brain trauma
- Strict emotional shock or stress.
- Stroke or brain infection
- Alcohol or drug misuse
What Is Dementia Disease?

Dementia does not mean forgetfulness. What is dementia disease is often misunderstood—it is a progressive disorder that influences the way a person thinks, perceives information, and lives daily. At the initial stages, the symptoms can be manifested in the form of mild memory lapses or sometimes confusion. In the long term, dementia affects communication, the decision-making process, emotional control, and the ability to conduct usual activities. In comparison with amnesia, dementia has a slow onset and is a disease that influences a variety of cognitive processes, which frequently results in a lack of independence and an increasing requirement for long-term care and assistance.
Dementia Symptoms
- Temporary memory loss, which gets worse with time.
- Practical and verbal communication impairments.
- Loss of track of dates, locations, or established schedules.
- Making bad choices and decisions.
- Mood swings, anxiety, or personality alteration.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Damage to the vessels due to heart diseases or strokes.
- Lewy body dementia and Parkinson’s-related dementia.
- Aging and genetic factors often increase the challenges faced by the elderly.
- The chronic diseases, such as diabetes or hypertension.
Key Differences Between Amnesia vs Dementia
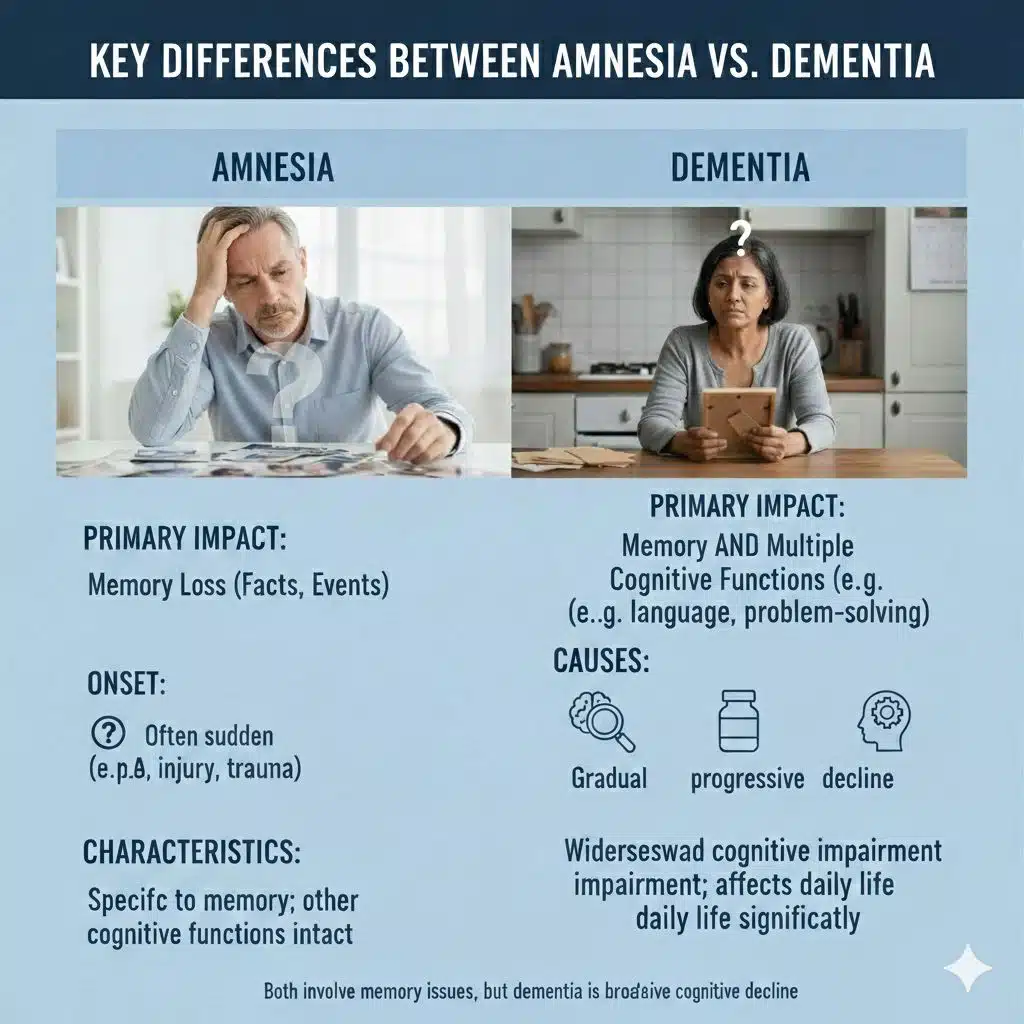
Even though both states come with the loss of memory, the differences between dementia vs amnesia can be seen when considering the way they develop as well as the extent to which they influence everyday lives.
Onset and Progression
- Amnesia: acute, can be associated with a particular event, and can be improved.
- Dementia: It is a slow, progressive deterioration that gets worse with time.
Memory Types Affected
- Amnesia: Retrograde/anterograde memory lapses.
- Dementia: Short-term, long-term, and procedural memory.
Cognitive and Daily Impact of Life.
- Amnesia: This is usually not associated with reasoning, personality, and everyday skills.
- Dementia: Impact on communication, judgment, self-care, and independence.
Causes
- Amnesia: Trauma, damage, stress, infection.
- Dementia: Neurodegeneration, Alzheimer’s, vascular conditions.
Amnesia vs. Dementia: How to Recognize the Early Symptoms
Amnesia symptoms usually come out suddenly, e.g., lack of memory without loss of personality or loss of thinking capacity.
Dementia symptoms occur gradually and involve progressive confusion, inability to cope with daily activities, and changes in behavior. Avoiding these patterns at an early stage can enable families to obtain medical assessment in time.
How Amnesia and Dementia are Diagnosed
The diagnosis should be done properly since the treatment and care plans are very different when compared between the two conditions.
Diagnosing Amnesia Disease
- History of injuries, trauma, or medical history.
- Memory and neurological examinations.
- Brain scans, MRI, or CT.
- Blood tests to eliminate infections and deficiencies.
Diagnosing Dementia Disease
- Memory, language, and reasoning cognitive testing.
- Daily activity functional assessment.
- To detect degeneration in the brain, brain scans are used.
- Continual observation of the symptoms.
According to the National Institute of Aging, diagnosing memory disorders like dementia involves neurological evaluations, cognitive testing, and brain imaging.
Treating Memory Loss of Amnesia and Dementia
The treatment aims at enhancing the quality of life and symptom management as opposed to a one-shoe-fits-all end point.
Managing Amnesia Disease Symptoms
- Addressing the underlying medical issue.
- Memory exercises in cognitive therapy.
- Reduction of stress and emotional support.
- Reminding, taking notes, and using electronic tools.
Daily Management for Dementia Disease
- Medications to slow cognitive decline
- Integrated steps to lessen chaos.
- Mental activity and interaction.
- Provision of professional caregiver support and family support.
Practical Tips for Living with Memory Loss
- Maintain a consistent daily routine
- Use calendars, alarms, and written reminders
- Encourage gentle physical and mental activity
- Create a safe and familiar living environment
- Seek professional support early
Why Choose Gracias for Senior Care
Gracias provides caring, dignified senior treatment and operates as a trusted dementia care home with a focus on the elderly with a memory deficit. Gracias enables seniors to keep their dignity, safety, and comfort, along with providing peace of mind to the families with trained caregivers, routines, and emotional support.
Conclusion
Learning about the differences between amnesia vs dementia will help you respond to the changes in memory calmly and appropriately. Whereas amnesia is sudden and can be recovered, dementia is chronic and needs long-term planning. Early identification and care are critical in improving mental health in the elderly and overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between amnesia vs dementia?
Amnesia mainly affects memory and often appears suddenly, while dementia causes a gradual cognitive decline affecting daily life.
What are the symptoms of amnesia?
Memory gaps, difficulty forming new memories, confusion about events, and repeated questions.
What are the symptoms of dementia disease?
Progressive memory loss, confusion, communication problems, poor judgment, and personality changes.
Can amnesia turn into dementia?
Amnesia itself does not turn into dementia, but severe brain damage may increase dementia risk.
How is amnesia diagnosed?
Through a review of medical history, neurological exams, brain imaging, and memory assessments.




